• Bangladesh •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
Natural disasters like flood and drought occurs almost every years in Bangladesh. In recent years (2004 and 2007) the occurrence of flood in this basin hampers the
development of the country. Moreover, there is a shortage of observational data hampers proper monitoring of flood situation and utilization of forecasting techniques.
The inundation areas are widely extended through the country.
- River Basin Name: Meghna
- River Basin Area: 61,021 km2
- Major Issues: Floods, Droughts
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident: Major floods on 2004.07.24 and 2007.08.04
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: To set-up a hydrological & flood inundation model, use of
satellite data and downscaling techniques.
- Objectives: The main goal is to achieve flood forecasting using a hydrological model and inundation areas in order to obtain an
optimal flood warning system and evacuation plan.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate
Semi-arid Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): -24 m; 480 m; 3817 m.
- Annual Average Precipitation: At Meghalaya Hills higher than 3000 mm.
- Dominant Land Use: Agriculture and Forest
- Dominant Soil Type: Loam-clay
- Geographic Coordinates: 90.5° - 92.5°E; 23.25° - 25.25°N
- River Basin Map:
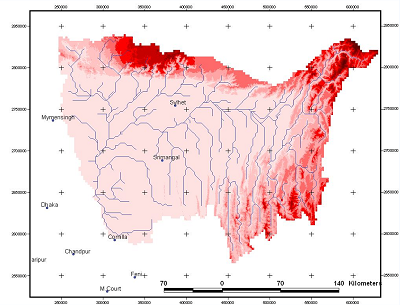
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 2 | Stream Flow | 18 |
| Humidity | 2 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | 38 |
| Wind | 2 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 2 | Evaporation | 2 |
| Precipitation | 44 | Soil Temperature | 2 |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | 2 |
| Skin Temperature | RCM data | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | RCM data | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | RCM data | Pilot Balloon | 1 |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | RCM data | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | RCM data | Radar | 1 |
| Net Radiation | RCM data | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | RCM data | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | RCM data | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | RCM data | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | Groundwater Well | 20 |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: none
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: Convective Stratiform Technique (CST)
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): none
- Data Intergration System: none
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: CST, Flood forecasting and warning center
Used mainly for: Floods
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Bhutan •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
The river basin is the second largest in Bhutan and very important from an economic point of view. Punakha-Wangdue is one of
the most fertile valleys. In addition, the biggest hydropower plants are also planned in this basin. On the other hand, the
frequent glacier melt increases the risk of glacial lake outburst floods (GLOF) and then decreasing flow in the rivers afterwards.
- River Basin Name: Punatsangchhu
- River Basin Area: 13,263 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident: Flood due to glacial outburst in October 1994
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) Flood forecast, (ii) Impacts of the hydropower generation,
and (iii) A sediment transport study
- Objectives: Determination of an adequate warning system for floods and assist in monitoring the flow regimes in
the rivers due to climate change.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 200 m (min), 6500 m (max)
- Annual Average Precipitation: 500 mm at foothills and above 5000 mm in upper reaches.
- Dominant Land Use: Agriculture
- Dominant Soil Type: It varies
- Geographic Coordinates: 89°21’- 90°24E ; 26°42’- 28°18N
- River Basin Map:
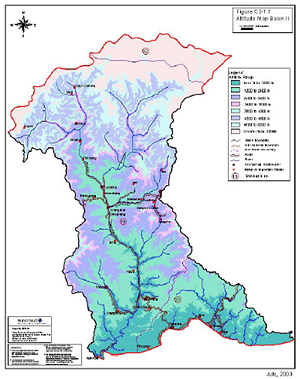
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 17 | Stream Flow | 5 |
| Humidity | 17 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | 4 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | | Evaporation | 5 |
| Precipitation | 17 | Soil Temperature | 5 |
| Snow Depth | 3 | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | 4 | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | 1 |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | 1 |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: available
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: available
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): available
- Data Intergration System: none
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: none
Used mainly for: ---
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Cambodia •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
It is one of the tributaries of Tonle Sap Lake, located in Battambang Province at southwest of Cambodia. Two hydropower stations are being planned at its upper basin.
The middle basin is covered with mixed agriculture and urban area and suffered from flash flood. The downstream region is inundated for 6month in a year by the
flood from Tonle Sap Lake and floating rice is cultivated.
- River Basin Name: Sangker
- River Basin Area: 2961 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident:
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) Impact of changes in the demands of water intake and dams → basin simulation model; (ii) Impact of changes
in climate, water resources, land cover → hydrological model; and (iii) Impact of changes in the canal level, sediment, flooding, river works → hydrodynamic model.
- Objectives: To study the impact of flash flood in case of heavy rains and to manage the water resources. By using the three model outputs, the impacts
on the environment and socio-economics will be addressed.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation):
- Annual Average Precipitation:
- Dominant Land Use:
- Dominant Soil Type:
- Geographic Coordinates: 102.5° - 104.0°E, 12.5° - 13.5°N
- River Basin Map:
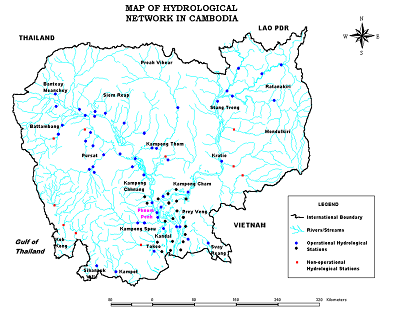
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | available | Stream Flow | available |
| Humidity | available | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | available | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | | Evaporation | |
| Precipitation | available | Soil Temperature | |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | available | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: SWAT, IQQM, ISIS
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: none
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): DEM with 50 m grid resolution
- Data Intergration System: Sharing Hymos Database
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: none
Used mainly for: Floods, IWRM
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• India •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
It is the largest tributary of Mahanadi basin. It rises in the Chandrapur district of Maharashtra at an elevation of about 532m and meets
Mahanadi river after traversing a distance of about 383 km.
- River Basin Name: Seonath
- River Basin Area: 30,760 km 2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident:
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration:
- Objectives: The objective of the project is to provide Quantitative Precipitation Forecast (QPF) and Probability of Precipitation (POP)
of the basin by downscaling technique (MOS, PPM, neural network etc) using the NWP model products and other data to the station/basin level. The accuracy of QPF should
be high enough so that it can be used in flood forecasting model (at least 80%).
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation):
- Annual Average Precipitation:
- Dominant Land Use: Cultivation (72%)
- Dominant Soil Type:
- Geographic Coordinates: 80.5° - 82.5°E, 20° - 23°N
- River Basin Map:
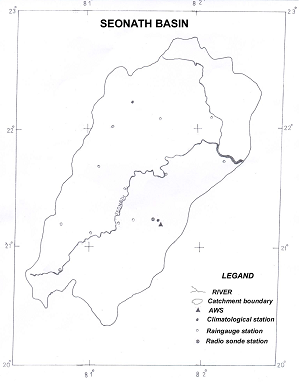
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 2 | Stream Flow | |
| Humidity | 2 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | 2 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 1 | Evaporation | 1 |
| Precipitation | 11 | Soil Temperature | 1 |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | 1 |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | 1 |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: none
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: none
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset):
- Data Intergration System: none
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: To be developed through this project.
Used mainly for: Floods
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Indonesia •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
Annual flood is occurring during rainy season and nowadays also during drought season, due to Indonesia lay on the monsoon climate zone. Regarding to that,
information system is required to inventory and process data about flood occurrence as information for decision-maker to take the right action in managing the flood.
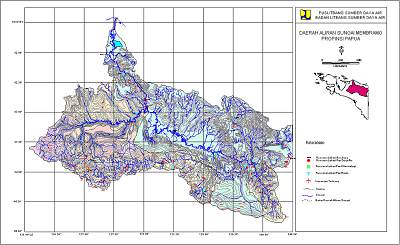
- River Basin Name: Mamberamo
- River Basin Area: 78,992 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident:
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) To take advantage of GIS database system and (ii) to support floods decision-makers.
- Objectives: A system is required to forecast floods in order to reduce their effects.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 0 m (min), 5000 m (max)
- Annual Average Precipitation: 3500 mm to 5000 mm
- Dominant Land Use: Tropical forest in upper parts; swamps in lowlands.
- Dominant Soil Type:
- Geographic Coordinates: 136.3º - 140.82ºE; 1.45º - 4.53ºS
- River Basin Map:
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 1 | Stream Flow | 2 |
| Humidity | 1 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | 1 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 1 | Evaporation | |
| Precipitation | 1 | Soil Temperature | |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | 1 | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | 1 | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | 1 |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: none
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: none
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): Digital river basin map
- Data Intergration System:
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: none
Used mainly for: ---
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Japan •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
It is located in the northern headwaters of the Tone river basin. The Tone river is a very important source of water supply, irrigation and power generation for the Tokyo area. Therefore
its management is crucial for the region. According to Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), the trend of frequency and intensity of heavy rainfall in this region has been increasing on
average from 1961-2001.
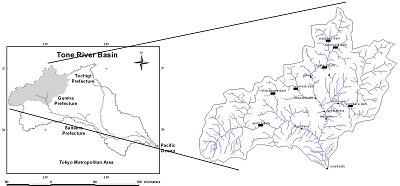
- River Basin Name: Upper Tone River
- River Basin Area: 3300 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident: September 1947, 171 mm/h caused by a typhoon, 1.6 million people affected.
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: A system able to (i) reduce flood peaks at downstream and (ii) replenish water levels in reservoirs
after a flood event by using quantitative precipitation forecast will be developed. The error forecast will be also considered by the bets means.
- Objectives: Release schedule of dams during extreme events does not follow manual, rather the experiences of dam operators are required.
Therefore, a system that can support them will be developed.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 100 m, 1020 m, 2500 m
- Annual Average Precipitation: 1500 mm
- Dominant Land Use: Forest (79.3 %) and Grasslands (9.5 %)
- Dominant Soil Type: Forest soil (56%), Black soil (22%), High permeable soil (15%).
- Geographic Coordinates: 138.2º - 139.6ºE, 36.2º - 37.2ºN
- River Basin Map:
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 4 | Stream Flow | 12 |
| Humidity | 4 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | 6 |
| Wind | 4 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 4 | Evaporation | |
| Precipitation | 27 | Soil Temperature | |
| Snow Depth | 1 | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | 1 |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: GBHM, WEB-GBHM
- Land Surface Scheme: SiB2
- Meteorological Model: Meso-scale Grid Point Data (MSM-GPV)
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): 50-m DEM, 100-m digital land use, digitized 1:200,000 soil maps,
hydrological thematic maps (slope, river network, and soil depth)
- Data Intergration System: DIAS
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: none
Used mainly for: Floods
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Korea •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
There have been significant damages from floods and flash floods in Korea. In addition to flood control works, some other non-structural countermeasures should be considered. The study area is
located at the middle-east of Korean Peninsula. It is an upper part of South Han River and the outlet is at Chungju-dam, which is the largest multi-purpose dam in South Han River basin.
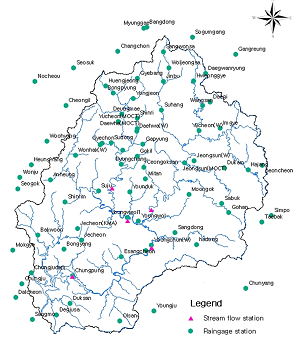
- River Basin Name: Upper Chungju-dam
- River Basin Area: 6662 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident:
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) The use of satellite data for flood and drought monitoring and prediction for enhancement of the existing system;
(ii) Utilization of an integrated hydrological and meteorological forecast system for the optimal dam operation and flood risk reduction.
- Objectives: Understanding of the regional and global water cycle mechanisms in case of climate change.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 0 m (min), 1561 m (max)
- Annual Average Precipitation:
- Dominant Land Use: Mountains covered by coniferous and deciduous forests
- Dominant Soil Type:
- Geographic Coordinates: 127.92º - 129.02ºE, 36.79º - 37.82ºN
- River Basin Map:
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 3 | Stream Flow | 5 |
| Humidity | 3 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | 1 |
| Wind | 3 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 3 | Evaporation | 3 |
| Precipitation | 46 | Soil Temperature | 3 |
| Snow Depth | 3 | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | 3 | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | available |
| Net Radiation | 3 | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | 8 |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | 26 |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: Storage Function Model
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: The global data assimilation and prediction system (GDAPS) for GCM models and the regional data assimilation and prediction
system (RDAPS) for regional climatic models
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): various data such as soil, vegetal covers, landuse, DEM, etc.
- Data Intergration System:
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique:
Used mainly for: Floods
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Lao PDR •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
It is located in Khammouane Province. At the source, the river flows from the Vietnam border in the southeast-northwest direction to Boualapha District and changes direction to
the west to Mahaxay District and then turns from the northeast-southwest into the Mekong. With an annual increase of 2.6% since 1990, the total population in the basin is estimated
to reach 192,200 in 1998.
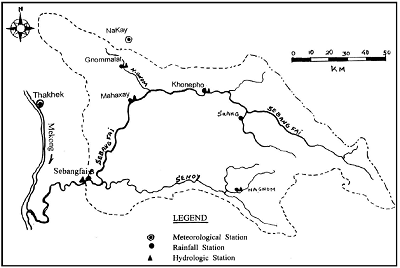
- River Basin Name: Sebangfai River
- River Basin Area: 8560 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident:
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) Capacity building of the staffs of Department of Meteorology and Hydrology in making a more accurate flood
forecasting and analysis; (ii) Assessment of the current conditions of hydro-meteorological stations; (iii) Discussion on how to improve the current data transmission system and the operation
and maintenance of these stations
- Objectives:
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 150 m (min), 1397 m (max)
- Annual Average Precipitation: 2300 mm
- Dominant Land Use: Forest (59%), Paddy (20%), Upland crops (10%)
- Dominant Soil Type: Mesozoic, Cretaceaus, Jurassic, and Palaezoic
- Geographic Coordinates: 105º - 106.5ºE, 17º - 18ºN
- River Basin Map:
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 1 | Stream Flow | 3 |
| Humidity | 1 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | | Evaporation | 1 |
| Precipitation | 5 | Soil Temperature | 1 |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | 2 |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | 2 |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: none
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: none
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): none
- Data Intergration System: none
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: none
Used mainly for: ---
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
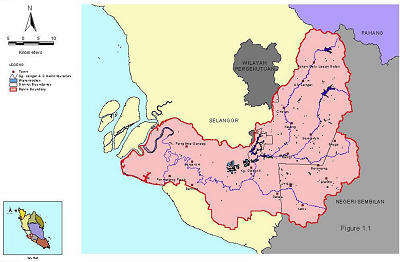
• Malaysia •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
Langat River Basin is one of the four major basins in Selangor State. Langat Dam is the major source of domestic water supply for Kuala Lumpur, Putrajaya and areas adjoining to it.
Groundwater extraction for industrial use is the minor water source of the basin. The Malaysian Government Administrative Centre Putrajaya is located at the centre of the basin.
- River Basin Name: Langat
- River Basin Area: 2350 km2
- Major Issues: Floods, Drought, Water Quality
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident: Severe drought and water crisis in 1998.
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) Impact of climate change and land use change on hydrology, water resources and socio-economic activities
(HydroClimate Model); (ii) Impact of changes in the demands of water intake and dam (Basin Simulation Model); and (iii) Impact of changes in the sediment, river level, flooding, river
networks (Hydrodynamic Model)
- Objectives: The main goal is to achieve reservoir inflow and water intake forecasting, flood and drought forecasting, and the impact of climate and land use
changes on the resources, environment and socio-economics of the basin.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 0 m, 40 m, 100 m
- Annual Average Precipitation: 2470 mm
- Dominant Land Use: Agriculture, Urban Area and Forest
- Dominant Soil Type: Sandy Clay
- Geographic Coordinates: 101°17' - 101°53'E; 2°40' - 3°09'N
- River Basin Map:
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 11 | Stream Flow | 6 |
| Humidity | 11 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | 1 |
| Wind | 1 | Groundwater Table | 30 |
| Pressure | 1 | Evaporation | 7 |
| Precipitation | 35 | Soil Temperature | |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | 1 | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | 1 | Pilot Balloon | 1 |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | 1 | Radiosonde | 1 |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | 1 | Radar | 1 |
| Net Radiation | 1 | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | 30 |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | 30 |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: none
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: none
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): none
- Data Intergration System: none
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: none
Used mainly for: ---
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
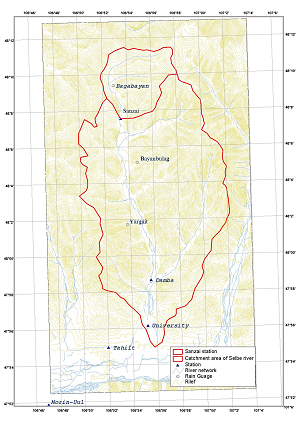
• Mongolia •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
The selected Selbe rive basin is located in center of Mongolia, in the north of Ulaanbaatar. It is the upper basin of the Tuul Stream basin (6300 km2).
From mid of 90-ties, settling area and population have been rapidly increasing. Following the human activities, individual house building, paved areas,
groundwater wells and livestock pasture are in creasing. Also forest cut and cultivation took place in some extent.
- River Basin Name: Selbe
- River Basin Area: 303 km2
- Major Issues: Floods, Droughts, Water Quality
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident:
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) Environmental degradation (vegetation, soil degradation, deforestation and rapid urbanization impacting on surface
and ground water regime and interaction mechanism, ground water contamination, water scarcity and flood control); (ii) Surface and ground water monitoring and modeling to assist better
management in light of anthropogenic influences and climate change impact and flood control; and (iii) Assistance in the development of information systems for promoting the implementation of
integrated water resources management (IWRM) in the Selbe and Tuul Stream Basins.
- Objectives:
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation):
- Annual Average Precipitation:
- Dominant Land Use: Forest (59%), Urban, Pasture
- Dominant Soil Type: Brown and Podzol
- Geographic Coordinates: 106.8º - 107.0ºE, 47.9º - 48.3ºN
- River Basin Map:
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 2 | Stream Flow | 2 |
| Humidity | 2 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | 2 | Groundwater Table | Not yet defined |
| Pressure | 2 | Evaporation | |
| Precipitation | 6 | Soil Temperature | 1 |
| Snow Depth | 1 | Soil Moisture | 1 |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | 1 (Ulaanbaatar, 0800LT & 2000LT) |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | 1 |
| Net Radiation | 1 | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | 1 | Groundwater Quality Indicators | Not yet defined |
| Latent Heat Flux | 1 | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: Linear regression model, Muskingum flood routing, Unit hydrograph model
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: none
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): DEM, river network, topography
- Data Intergration System: none
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: none
Used mainly for: ---
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
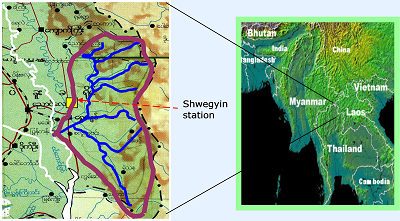
• Myanmar •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
Shwegyin town is situated on the mouth of Shwegyin River and composed of 8 wards and 26 villages. It is about 42 miles from north to south and 19 miles from east to west.
The high mountains are formed in northern and eastern part and plain areas are in the western and southern part of the basin. There are 5 rivers flowing through the township
including Shwegyin River.
- River Basin Name: Shwegyin
- River Basin Area: 1747 km 2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident: 2650 mm/40 hours 1997.08. 30,870 persons, 6050 m2 area of paddy field
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) To install two telemeter stations and a receiving station in Shwegyin basin; (ii) To develop forecasting technique
for flash flood; and (iii) To develop accurate flood inundation maps using all available data including GIS data sources.
- Objectives: To get early flood warning system for the Shwegyin River Basin.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 12 m, 951 m, 1890 m
- Annual Average Precipitation: 3552 mm
- Dominant Land Use:
- Dominant Soil Type:
- Geographic Coordinates: 96.75º - 97.167ºE, 17.5º - 18.5ºN
- River Basin Map:
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 1 | Stream Flow | 1 |
| Humidity | 1 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | 1 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 1 | Evaporation | |
| Precipitation | 1 | Soil Temperature | |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model:
- Land Surface Scheme:
- Meteorological Model: Multilinear regression
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset):
- Data Intergration System:
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: Flood frequency analysis, stage correlation
Used mainly for: Floods
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
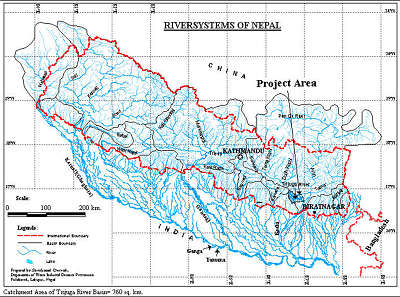
• Nepal •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
Bagmati river originates from the southern slopes of Shivapuri Lekh at Vagdhara, north of Kathmandu. It flows towards south west from its origin and turns to west in Kathmandu city and
emerges out of Kathmandu Valley at Chovar. The maximum flood discharge observed is about 11,000 m3/s.
- River Basin Name: Bagmati
- River Basin Area: 3700 km2
- Major Issues: Floods, Water Quality
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident: Rain 540 mm on July 20, 1993 caused extensive damage, 200 deaths.
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) Reduce flood damages: bank erosion and inundation; (ii) Reduce landslides and debris flows by
means of landslides hazard mapping; and (iii) Water Pollution is crucial since it is used to meet the irrigation demand.
- Objectives: To develop an effective flood and rainfall prediction system including disaster management, resource management,
resource allocation and environmental conservation.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid (sub-tropical) Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): Middle Mountain, highest 2740 m
- Annual Average Precipitation:
- Dominant Land Use: Forest
- Dominant Soil Type:
- Geographic Coordinates: 85º - 86ºE, 27.83º - 26.75ºN
- River Basin Map:
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 11 | Stream Flow | 3 |
| Humidity | 4 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | 4 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 4 | Evaporation | 2 |
| Precipitation | 25 | Soil Temperature | 2 |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: HEC Model
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: Not available
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): Transportation networks, contours, settlement area, administrative boundaries,
land use, river system.
- Data Intergration System: Started archiving data sets such as LANDSAT, SRTM DEM.
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: On-going development, CDMA
Used mainly for: Floods
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Pakistan •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
- River Basin Name: Swat
- River Basin Area:
- Major Issues:
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident:
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration:
- Objectives:
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation):
- Annual Average Precipitation:
- Dominant Land Use:
- Dominant Soil Type:
- Geographic Coordinates:
- River Basin Map:
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | | Stream Flow | |
| Humidity | | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | | Evaporation | |
| Precipitation | | Soil Temperature | |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model:
- Land Surface Scheme:
- Meteorological Model:
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset):
- Data Intergration System:
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique:
Used mainly for:
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Philippines •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
The selected Pampanga river basin is the forth largest basin in the Philippines. The total length of the main river is about 260 km. The basin is drained through the Pampanga River and via
the Labangan Channel into the Manila Bay. The main river is supported by several tributaries. It has a relatively low-gradient channel at the middle and lower sections. There are two
dams within the river basin.
- River Basin Name: Pampanga
- River Basin Area: 10,540 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident:
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) Downscaling and (ii) Optimal multi-purpose reservoir operation
- Objectives: End-to-end approach in water resources management (IWRM)
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 100 m (min), 1115 m (max)
- Annual Average Precipitation: 4200 mm
- Dominant Land Use:
- Dominant Soil Type:
- Geographic Coordinates: 120.5º - 121.5ºE, 14.75º - 16.25ºN
- River Basin Map:
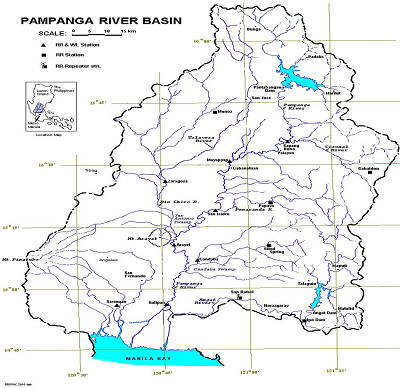
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 2 | Stream Flow | 2 |
| Humidity | 2 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | 2 |
| Wind | 2 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 2 | Evaporation | 1 |
| Precipitation | 10 | Soil Temperature | |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: WATBAL Hydrologic model
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: none
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): none
- Data Intergration System: none
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: none
Used mainly for: Floods
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Sri Lanka •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
The Kalu (River) Ganga basin is located at the South-Western part of Sri Lanka. It is about 130 km long and discharges into the Indian Ocean. The flood disasters continue in
the basin due to climatic, hydrologic, topographic and land use characteristics in the basin. There is a hydropower reservoir at one of the upper reaches.
Population density in Kalutara and Ratnapura districts are 677 and 314 person/km2.
- River Basin Name: Kalu Ganga
- River Basin Area: 2720 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident:
| District | Affected Families | Deaths | Houses destroyed | Houses partially damaged |
|---|
| Kalutara | 21,550 | 8 | 7658 | 35 |
| Ratnapura | 47,756 | 137 | 5726 | 6902 |
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) Flood risk reduction; (ii) Identification of inundation levels; and (iii) Implementation of early
warning systems based on real time flood forecasting.
- Objectives: To minimize flood damages by using DHM & RS.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 2250 m (max)
- Annual Average Precipitation: 3000 mm
- Dominant Land Use: Tropical rain forest
- Dominant Soil Type:
- Geographic Coordinates: 80.00º - 80.67ºE, 6.42º - 6.83ºN
- River Basin Map:
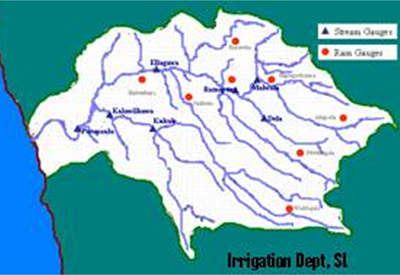
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 1 | Stream Flow | 2 |
| Humidity | 1 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | 1 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 1 | Evaporation | 1 |
| Precipitation | 10 | Soil Temperature | 1 |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: One-dimensional hydraulic model
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: none
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): DEM, land use and river network
- Data Intergration System: none
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: none
Used mainly for: Floods
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Thailand •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
Mae Wang Basin is one of the sub-basins of the Mae Ping Basin in Northern Thailand. Most of the basin is mountain area declining from west to east that consists of the
mixed unit of steep slope highland soil series.
- River Basin Name: Mae Wang
- River Basin Area: 600 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident:
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) To install telemetering station for observation and collection of Hydro-meteorological data;
(ii) Developing a flood warning model and effective water management
- Objectives: Flood forecast and early warning system
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 300 m, 1000 m, 2500 m
- Annual Average Precipitation:
- Dominant Land Use: Forest and agriculture
- Dominant Soil Type: Mixed unit of steep slope highland soil
- Geographic Coordinates: 98.5º - 98.83ºE, 18.583º - 18.75ºN
- River Basin Map:
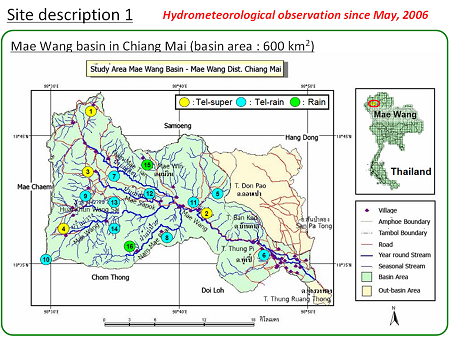
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 13 | Stream Flow | 5 |
| Humidity | 4 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | |
| Wind | 4 | Groundwater Table | 4 |
| Pressure | 4 | Evaporation | |
| Precipitation | 15 | Soil Temperature | 10 |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | 10 |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | 4 | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | 4 | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | 4 | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | 4 | Radar | |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: Stage correlation model
- Land Surface Scheme: SiBUC, MATSIRO
- Meteorological Model: MM5
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): River line, Land use, Soil type, 20-m contour line, point of village, road line
- Data Intergration System: Water cycle information integrative system (UT)
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: None
Used mainly for: Floods
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Uzbekistan •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
The selected Chirchik-Okhangaran basin is located in northeastern part of Uzbekistan. Snowmelt induced runoff of rivers of the Chirchik – Okhangaran basin comprised 60-90% of
the total stream flow. In the Chirchik - Okhangaran river basins have 19 hydropower stations. There are two rivers – Chirchik (161 km) and Okhangaron (223 km). River basin has
67 lakes with different genesis type. This basin has 2384.6 thousand people.
- River Basin Name: Chirchik-Okhangaran
- River Basin Area: 20,160 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident: Mudslide, 1969, March
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: (i) Sediment transport, (ii) impacts of hydrological processes and on hydropower generation,
and (iii) to monitor the flow regimes in the rivers due to climate change.
- Objectives: Determination of an adequate warning system for floods.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 400 m, 600 m, 4301 m
- Annual Average Precipitation:
- Dominant Land Use:
- Dominant Soil Type:
- Geographic Coordinates: 69.33º - 71.25ºE, 40.17º - 42.25ºN
- River Basin Map:
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 10 | Stream Flow | |
| Humidity | 10 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | 19 |
| Wind | 10 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 10 | Evaporation | 3 |
| Precipitation | 22 | Soil Temperature | 10 |
| Snow Depth | 23 | Soil Moisture | 3 |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | 2 |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | 2 | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | 2 | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: none
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: none
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): none
- Data Intergration System: none
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: none
Used mainly for:
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
• Vietnam •
--> Basin Description
1. Background, Issues, and Objectives
The Huong river basin belongs to the Thua Thien Hue province in coastal of the Central Viet Nam. The Huong river system contains 3 main rivers: Ta Trach, Huu Trach and Bo River.
The Huong River is short and steep runs from mountain to the low plain area. Time of concentration is short and river basin has low storage capacity. Floods and inundation
often occur very quickly and severely.
- River Basin Name: Huong
- River Basin Area: 2830 km2
- Major Issues: Floods
- Significant event whent the issues specified above were evident: Heavy rainfall induced flood; 2320 mm/3 days in November 1999
- Targets to be addressed through demonstration: To improve accuracy of the forecast, effective natural disaster preparedness,
prevention measures and reduce the losses.
- Objectives: To get efficient flood warning system.
2. River Basin Characteristics
- Climate Regime (highlight): Very Humid Humid Temperate Semi-arid
Arid Cold/Tundra
- Topography (minimum, maximum, average elevation): 500 m (min); 1000 m (max)
- Annual Average Precipitation: 3000 mm
- Dominant Land Use: Forest
- Dominant Soil Type: Erodible laterit soil
- Geographic Coordinates: 107º - 108ºE, 16º - 17ºN
- River Basin Map:
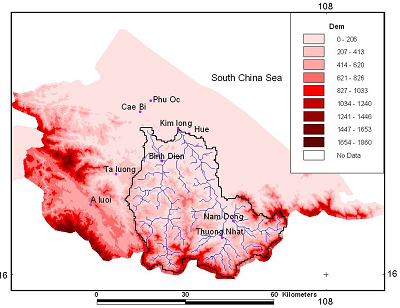
3. Observation System
| SURFACE | Number | HYDROLOGICAL | Number |
|---|
| Air Temperature | 3 | Stream Flow | 1 |
| Humidity | 3 | Reservoir (Water Level, Outflow) | 1 |
| Wind | 3 | Groundwater Table | |
| Pressure | 1 | Evaporation | 3 |
| Precipitation | 7 | Soil Temperature | 3 |
| Snow Depth | | Soil Moisture | 3 |
| Skin Temperature | | ATMOSPHERE | Number |
| Upward Shortwave Radiation | | Planetary Boundary Layer Tower | |
| Downward Shortwave Radiation | | Pilot Balloon | 1 |
| Upward Longwave Radiation | | Radiosonde | 1 |
| Downward Longwave Radiation | | Radar | 2 |
| Net Radiation | | WATER QUALITY | Number |
| Sensible Heat Flux | | Groundwater Quality Indicators | 15 |
| Latent Heat Flux | | Surface Water Quality Indicators | |
| Ground Heat Flux | | OTHERS | Number |
| CO2 Flux | | | |
4. Models, GIS, Data Integration System, Prediction System
- Hydrological Model: Multivariable regression, TANK, NAM, MARINE
- Land Surface Scheme: none
- Meteorological Model: none
- List of GIS Data at Fine Resolution (besides global dataset): 50 m DEM, land use, soil type, river network etc...
- Data Intergration System: HydroMet Data, Digital Hydrological database, Digital Meteorological database
- Type of Prediction System and Downscaling Technique: HRM, ETA and WBAR
Used mainly for: Floods
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
















